SUSTAINABILITY RESEARCH
Nutrient recovery from municipal wastewater for sustainable food production systems: An alternative to traditional fertilizers
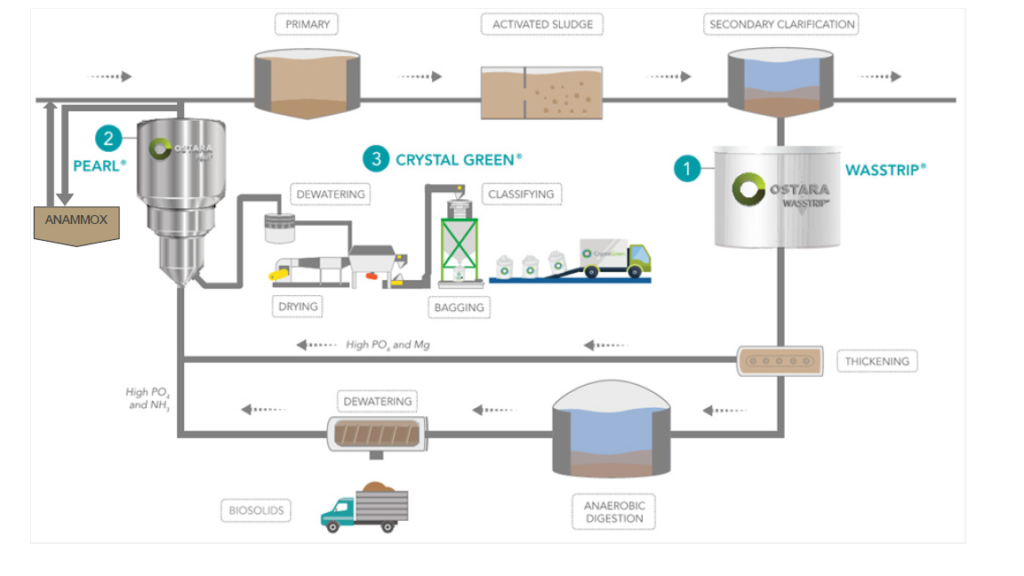
Traditional wastewater management uses end-of-pipe approaches to remove pollutants in wastewater before discharge. To address the question whether nutrient recovery is indeed a more efficient strategy from a system perspective and provides more benefits to society, this research compares fertilizer production from struvite to the traditional commercial fertilizers (e.g., diammonium phosphate, DAP). Emergy defined as the available energy required directly and indirectly through all transformations to make a product, process, or service is the tool used for system analysis in this study. Emergy accounting provides system analysis of total resource use and whole system efficiency. The results show that struvite production uses one order of magnitude less emergy than DAP production to produce one unit of fertilizer, indicating that struvite production is a more efficient process. This research sheds light on alternative nutrient management through nutrient recovery, which may achieve economic and environmental benefits and overall higher system efficiency.
Related Publication
- Theregowda, R. B., González-Mejía, A. M., Ma, X. (Cissy), & Garland, J. (2019). Nutrient Recovery from Municipal Wastewater for Sustainable Food Production Systems: An Alternative to Traditional Fertilizers. Environmental Engineering Science, 833–842. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2019.0053
Use Phase Energy Analysis for Conventional and Guayule Rubber Tire Compositions
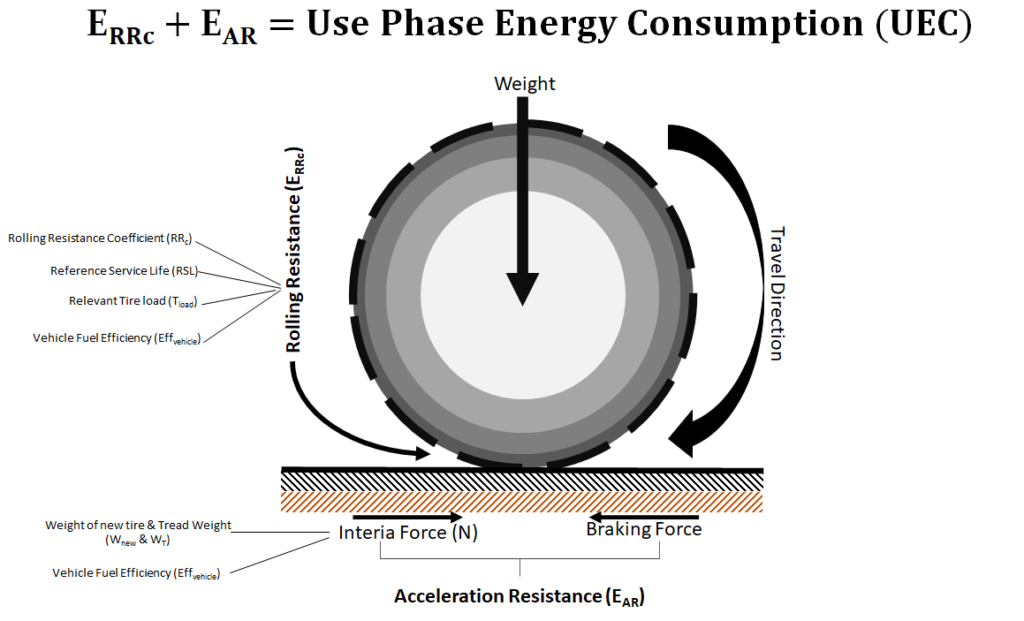
This study presented the first rolling resistance and use-phase energy consumption estimates for guayule tires. The results of this study show that use-phase life cycle energy reductions can be achieved with NRs and that the rolling resistance coefficient (RR cnew ) and reference service life (RSL) of the new tire are the critical parameters that pertain to energy and fuel efficiency. A tire’s use phase accounts for approximately 86% of its life cycle energy consumption and thus is an important consideration in sustainability assessments. We calculated the use-phase energy consumption for two types of NR tires: a 100% guayule rubber tire and an experimental epoxidized NR tire. These two NR tires were compared against a conventional passenger tire made by Cooper Tire & Rubber Company.
Related Publication
- Theregowda, R. B., Eranki, P. L., & Landis, A. E. (2019). ENERGY ANALYSIS OF THE USE PHASE OF CONVENTIONAL TIRES COMPARED TO GUAYULE NR TIRES. Rubber Chemistry and Technology, 578–588. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.19.81495
Application of Integrated LCA to Evaluate Tertiary Treatment Alternatives for Reuse of Treated Municipal Wastewater in Thermoelectric Power Plant Cooling Systems

As available freshwater becomes more limited, power plants are investigating alternative sources for recirculating cooling system make-up water, such as acid mine drainage, saline/produced water, and secondary treated municipal wastewater (MWW). Use of lower quality waters increases the challenges of managing cooling water chemistry to avoid scaling, corrosion, and biofouling in cooling system piping and heat exchange equipment. Such waters often require treatment prior to use in cooling systems, which may involve significant capital costs and maintenance requirements.
Related Publications
- Walker, M. E., Safari, I., Theregowda, R. B., Hsieh, M.-K., Abbasian, J., Arastoopour, H., Dzombak, D. A., & Miller, D. C. (2012). Economic impact of condenser fouling in existing thermoelectric power plants. Energy, 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.06.010
- Walker, M. E., Theregowda, R. B., Safari, I., Abbasian, J., Arastoopour, H., Dzombak, D. A., Hsieh, M.-K., & Miller, D. C. (2013). Utilization of municipal wastewater for cooling in thermoelectric power plants: Evaluation of the combined cost of makeup water treatment and increased condenser fouling. Energy, 139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.07.066
- Theregowda, R., Hsieh, M.-K., Walker, M. E., Landis, A. E., Abbasian, J., Vidic, R., & Dzombak, D. A. (2013). Life cycle costs to treat secondary municipal wastewater for reuse in cooling systems. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 224–238. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2013.078
- Theregowda, R., Vidic, R., Dzombak, D. A., & Landis, A. E. (2014). Life cycle impact analysis of tertiary treatment alternatives to treat secondary municipal wastewater for reuse in cooling systems. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 178–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11938
- Theregowda, R. B., Vidic, R., Landis, A. E., Dzombak, D. A., & Matthews, H. S. (2016). Integrating external costs with life cycle costs of emissions from tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater for reuse in cooling systems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 4733–4740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.020
A CENTURY Model Simulation of Soil Organic Matter (SOM) in Clear Creek Watershed, Iowa

This project was my M.Sc. thesis work that summarized a study dealing with numerical modeling of organic matter dynamics using a FORTRAN model to simulate and evaluate soil organic C and N trends for different crop rotation scenarios and geochemical parameters. My thesis work inspired me to learn further in-depth about the soil and water processes through investigation.
Related Publications
- Theregowda, R., Abaci, O., & Papanicolaou, A. N. (2006, May 19). The Use of Sediment Tracers in Watershed Processes. World Environmental and Water Resource Congress 2006. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2006. https://doi.org/10.1061/40856(200)413
Recycle and Reuse of Wastewater in Service Station

During my sophomore year, as a requirement for the degree, I worked to design a prototype to treat the service station wastewater for recycle and reuse in the service station. This project won 2nd place at the 7th National Convention of ISTE Students organized by the B&B Institute of Technology at Vidyanagar, Gujarat, India. In 2008, this project was also published as a book chapter in Environmental Science and Technology in India
Reduction of Inorganic Salts using Low Cost Attenuation Media
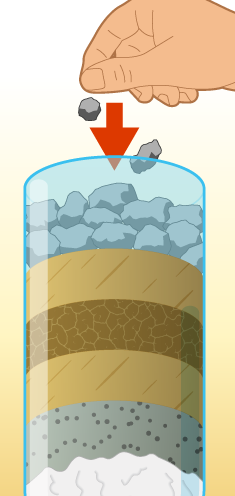
In the junior year of undergrad, I worked on a course project, wherein our team designed a 2 inch glass column filter that was filled with organic media (such as raw rice-husk or saw dust or coconut husk) and sand-gravel filtration media to reduce the inorganic salts from industrial groundwater samples. The organic media showed reduction up to saturation time, but needed to be constantly replaced as they had moderate to low attenuation capacity when used raw.
DATA SCIENCE
Bixi Project – Data Analysis in SQL and Visual Analytics in Tableau
Using SQL queries I generated insights from a real-world dataset stored in a relational database. As a visual analytics specialist, I created data visualizations using Tableau, allowing the user to interactively derive answers to business questions from the same dataset without having to write a code.
Stats and Politics – Cleaning, EDA and Data Analysis

Performed EDA and Data analysis for analyzing data from previous United States presidential elections. Statistical model developed to predict the popular vote in the U.S. presidential elections from 2016 showed 62% accuracy.
NLP With Hotel Review – EDA, Data Wrangling and Modelling

Performed sentiment analysis (counter vectorization) of hotel reviews to determine how to increase positive reviews. Used different model fits and performed feature engineering to determine improvement in prediction accuracy assessed using confusion matrix.
Hackathon – Securing the Future of Food Delivery with Skip the Dishes

Worked with a multi-disciplinary, cross-country team making food delivery sustainability goals realistic to customers and restaurants.
Food menu items should include a curated rating system called ‘Smart Score’ – factors influencing the rating – locally grown crops (total commodity supply), health/nutritional needs, distance delivered from and LCA emissions.
Big Data Wrangling with Google Books Ngrams

Applied skills learnt to load, filter, and visualize a large real-world dataset in cloud-based distributed computing environment using Hadoop, Spark, and the S3 filesystem.
Followed a Big Data analysis workflow to filter and reduce data down to a manageable size, and then do some analysis locally on local machine after extracting data from the Cloud and processing it using Big Data tools.
CAPSTONE: Predicting CO2 Flux and Storage in Boreal Forests
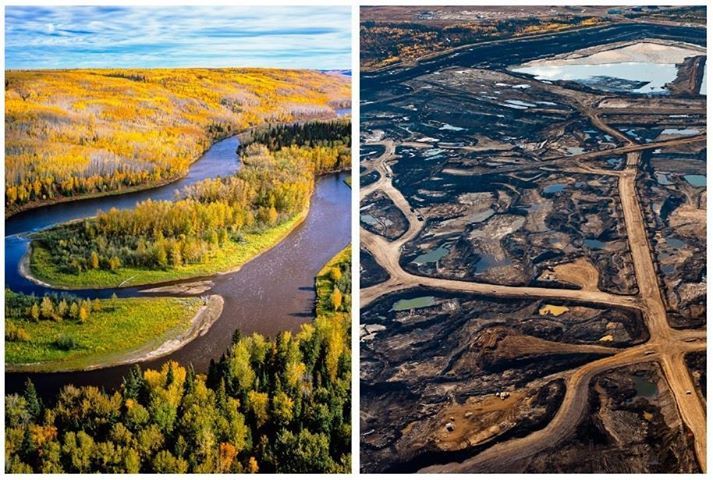

Image: Redbud Farms
Given that there are large data measurements to model the carbon (C) sequestration (absorption and emission of C) in the Boreal Forests ecosystem, the complexity involved in applying manual statistical analysis or linear models on large datasets can lead to failure in capturing important C trends. Consequently, to develop a model/method that can accurately capture and estimate the changes in the C trends due to advertent and inadvertent impacts of human activities, the current advances in data science tools, and techniques for organizing and analyzing large amounts of data needs to be effectively employed by environmental researchers and policy makers alike. Hence, this project aims to use data science modeling tools on the available data to capture the trends of the CO2 exchange (flux) and stocks (storage) for the Boreal Forests.
